Steady-state Solar Simul...
Steady-state solar simulators, also known as continuous solar simulators, are light sources that provide constant illumination over time. They are used to measure the output performance of solar thermal collectors and photovoltaic modules without being affected by weather conditions.
A solar simulator is a light source that has specific quantifiable similarities to natural sunlight, namely in its spectral distribution and intensity. It may also be referred to as an artificial sun or sunlight simulator.
The purpose of a solar simulator is to provide a consistent, controllable source of illumination in a laboratory environment. The most commonly discussed three areas of similarity are: spectral match, spatial non-uniformity, and temporal instability.
Readmore
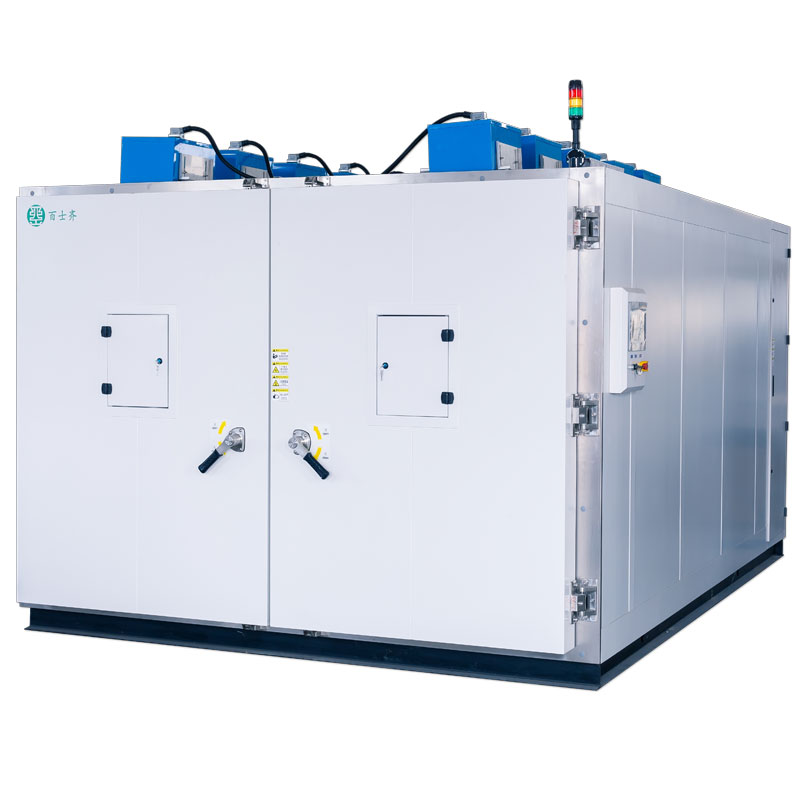
UV Preconditioning Test ...
UV preconditioning test chamber is an irradiance test that determines how susceptible solar panels are to UV deterioration and, as a result, performance loss
In PV modules, many different components are exposed to the sunlight. Therefore, the IEC 61215 defines a UV preconditioning test (MQT 10) to test at whether or not these elements can face up to the UV radiation of the sun. In our radiation chamber, the UV radiation is up to 5 times the solar depth to speed up the test, as requested in the UV preconditioning test. During the test, the module temperature is stored steady at +60°C in a distinct temperature chamber. We supply our UV light test chamber solutions which include the records acquisition unit, radiation and temperature sensors.
Readmore
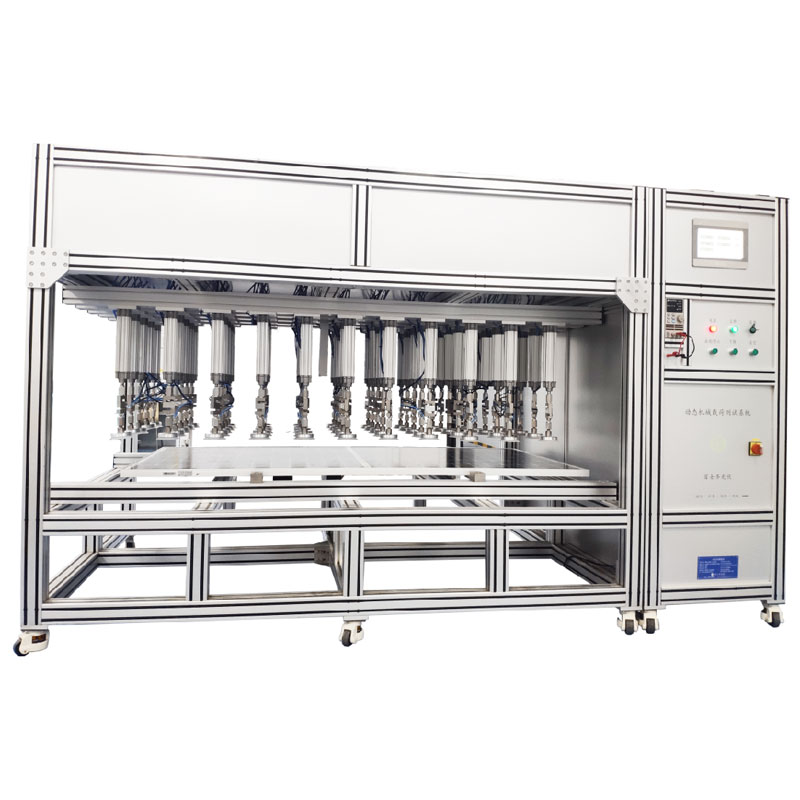
Static/Dynamic Mechanica...
Static/dynamic mechanical load tester simulates static and dynamic loads and is suitable for load testing according to international standards for modules of typical size. Our system operates using a series of programmed and pneumatically powered cylinders with suction to connect to the module. The cylinders move on a pre-determined test schedule that specifies the speed, force and duration of each test
Readmore
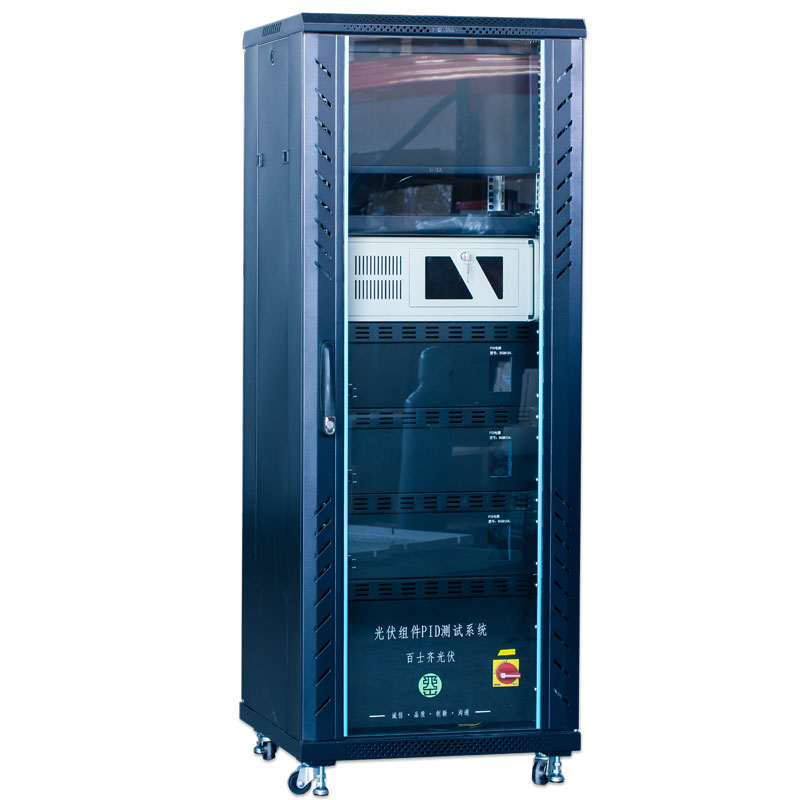
PID Tester
PID tester (potential induced degradation) is a type of deterioration that occurs in solar power generation systems. It is caused by leak current created by a large potential difference generated between a PV module frame and module circuit. PID is considered to be a factor responsible for solar power generation system output drops, and to be promoted by humidity. Accurate PID evaluation requires leak current measurement after applying a high voltage in a high-temperature/humidity environment with high precision and reproducibility.
Readmore
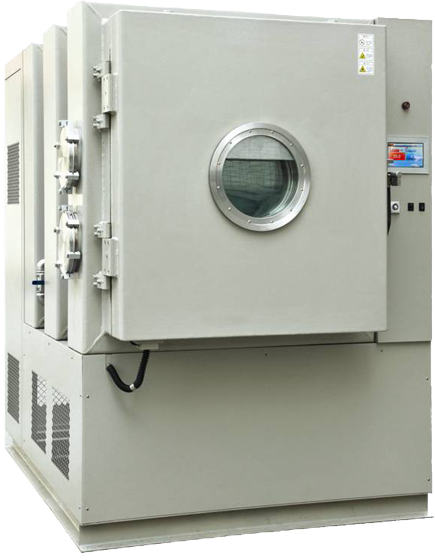
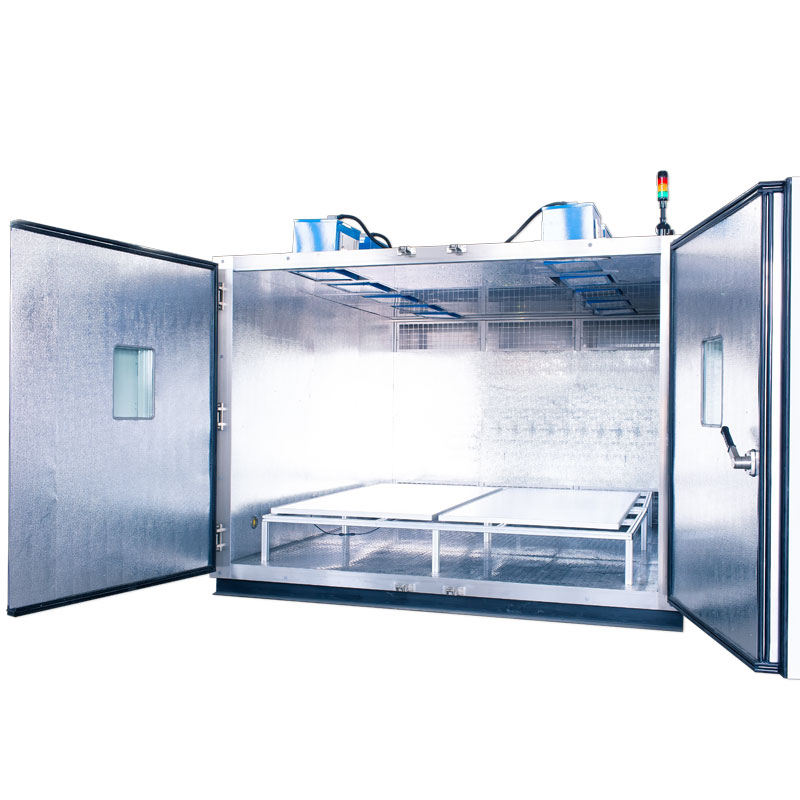
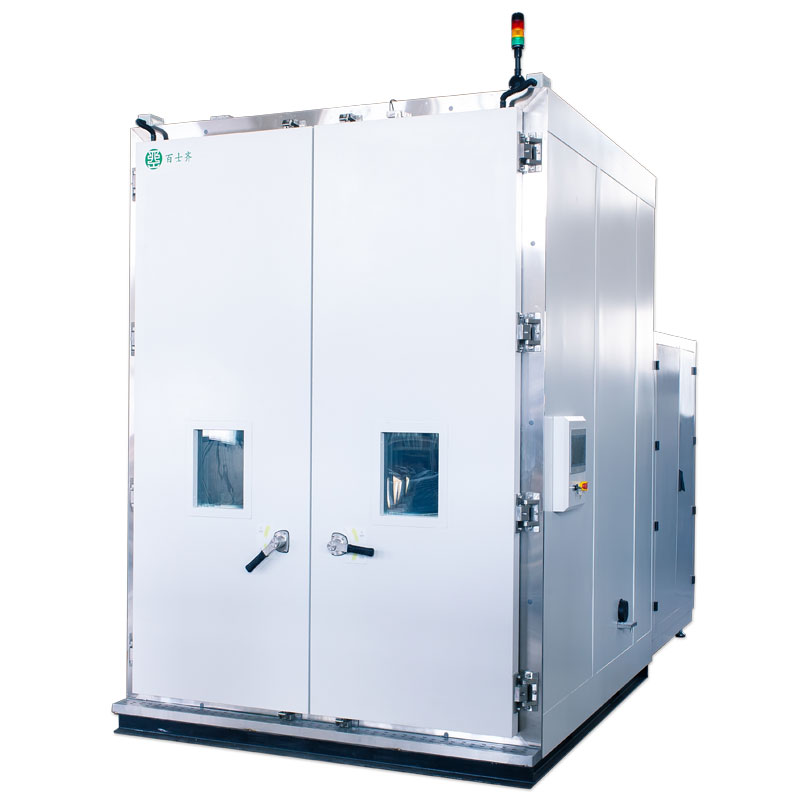
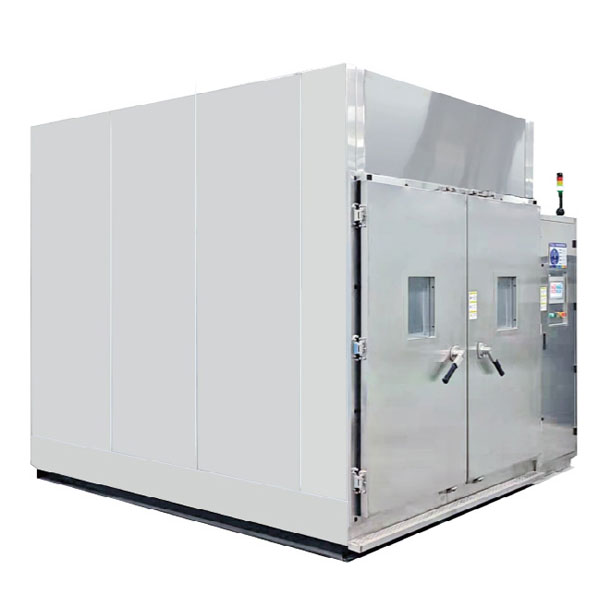
Environmental Chamber fo...
Environmental chamber for Thermal Cycling and Humidity-Freeze Test are environmental tests that can be used to evaluate the performance of PV modules in extreme weather
In Humidity-Freeze Test, PV modules are subjected to cycling between temperatures 85°C with relative humidity 85 % and -40°C. PV modules are subjected to 10 complete cycles in the closed climatic chamber in accordance with the profile on the picture bellow. The purpose is to determine the ability of the module withstand against humidity penetration.
Thermal cycling tests are done for PV module certification, a current within +/-2 percent of the current measured at the peak power when the temperature of the solar module is above 25° C should be injected. The tested solar module is subjected to the cycling temperature limits of an extreme low temperature of – 40°C ± 2°C and an extreme high temp of + 85°C ± 2°C .
Readmore
Salt Spray Test Chamber
Salt Spray Test Chamber determine the corrosion resistance of components and their packaging materials
Readmore